Building Cybersecurity Infrastructure for Regulatory Compliance: Essential Tools for Risk Mitigation

A robust cybersecurity infrastructure isn't a luxury. It's a necessity.
I'm in a unique position as a Chief Information Security Officer. I witness the ever-changing landscape of cybersecurity threats. Concern about these threats continue to escalate, but that's not all. Regulatory compliance, now vital for data protection and risk management, isn't just an add-on to cybersecurity-it's an integral part of it.
Cyberattacks often lead to compliance fines and litigation. This is particularly true in regions like the European Union, which has implemented strict data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This regulation not only emphasizes the pressing need for comprehensive cybersecurity for those handling personally identifiable information (PII), protected health information (PHI), or financial data, but also extends protections to other categories of sensitive data. These include biometrics, race, religion, IP addresses, marital status, and emails. Given such developments, integrating compliance as a key consideration in your cybersecurity strategy is becoming increasingly crucial, irrespective of your global location.
Understanding Asset Management
Asset management is foundational to ensuring your infrastructure can accurately report compliance with appropriate regulations. This is for several reasons:
- Asset Inventory: By having a comprehensive understanding of the assets, organizations can better protect and monitor them and ensure they meet the necessary compliance standards.
- Risk Assessment: Asset management enables organizations to assess the risk associated with each asset. It helps identify vulnerabilities, potential threats, and the impact of a security breach on critical assets, all of which are key components in many compliance regulations.
- Vulnerability Management: Identify which assets are running outdated or vulnerable software versions, making it easier to prioritize patch management and updates. This is crucial in maintaining compliance with many cybersecurity regulations.
- Incident Response: Organizations can quickly identify affected assets, isolate them from the network, and take appropriate actions to mitigate the incident's impact. Without proper asset management, incident response becomes challenging, and organizations may struggle to contain and remediate security breaches effectively. This could result in non-compliance and associated penalties.
- Compliance: Asset management is often a requirement for compliance with various regulations and standards, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) or the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Leveraging Endpoint Detection and Response
EDR solutions play a critical role in a compliance-centered cybersecurity strategy for several reasons:
- EDR solutions enable real-time monitoring and visibility, detecting advanced threats and sophisticated attacks. This assists in meeting compliance regulations that require prompt detection and response to threats.
- EDR solutions aid in compliance, providing evidence for incident reporting and legal proceedings if needed. This can be particularly crucial for organizations that are subject to regulations like GDPR, which require detailed reporting on data breaches.
Multi Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) helps not only to prevent cyber-attacks but also to meet certain compliance requirements that mandate additional layers of security beyond just usernames and passwords. Here's how MFA effectively combats various attack vectors and helps maintain compliance:
- MFA mitigates the risk of stolen credentials by requiring additional authentication factors, preventing unauthorized access with compromised credentials. This is particularly crucial for compliance with regulations that require robust access controls, such as HIPAA in the healthcare sector.
- MFA provides protection against credential reuse by requiring separate authentication factors for each account, preventing the exploitation of compromised credentials across multiple platforms. This can help meet compliance requirements that mandate unique credentials for different accounts.
- MFA complicates brute-force attacks by adding extra steps and requiring additional authentication factors, making it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access. Some compliance standards require defense mechanisms against such attacks.
- MFA acts as a defense against phishing attacks by not providing the required authentication factor on fake login pages, preventing successful authentication by attackers. In addition to enhancing security, this is also a component of many data protection regulations.
The Role of Cybersecurity Frameworks
A well-implemented cybersecurity framework not only enhances security but also facilitates regulatory compliance. Here are some ways a cybersecurity framework contributes to compliance:
- Guidance and Structure: Cybersecurity frameworks provide a structured approach to managing cybersecurity risks, which is often a requirement for regulatory compliance. For example, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides a set of standards, guidelines, and best practices for managing cybersecurity risk.
- Baseline Security Controls: Many cybersecurity frameworks include baseline security controls that organizations should implement. These controls often align with the requirements of various compliance standards.
- Continuous Improvement: Cybersecurity frameworks encourage continuous improvement and periodic assessment of cybersecurity practices, which is often a requirement for compliance. This helps organizations stay abreast of evolving threats and maintain compliance with changing regulations.
- Third-Party Risk Management: Cybersecurity frameworks often include guidance on managing third-party risk, which is an area of focus for many compliance standards.
- Documented Policies and Procedures: Most cybersecurity frameworks recommend that organizations document their cybersecurity policies and procedures. This documentation is often required for regulatory compliance.
Looking Ahead
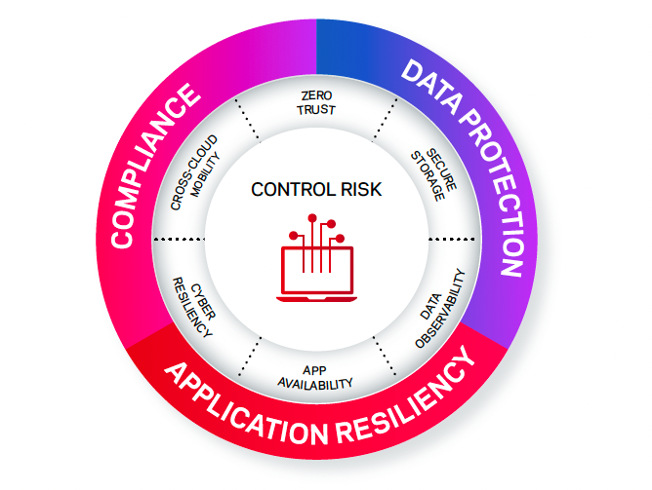
By embedding compliance into your cybersecurity strategy, you can create a robust security infrastructure that both protects against threats and ensures regulatory compliance. It's a two-pronged approach that not only helps prevent cyberattacks but also mitigates the risks and impacts of non-compliance.
Ultimately, compliance isn't just about ticking boxes—it's about understanding and mitigating risks. By integrating compliance considerations into your cybersecurity strategy, you'll be better equipped to navigate the evolving landscape of cyber threats and regulatory demands.
Explore ways to control risk and optimize data compliance.
Check out additional blogs from Veritas CISO, Christos Tulumba:
-2.png.transform/background-xl/img.png)